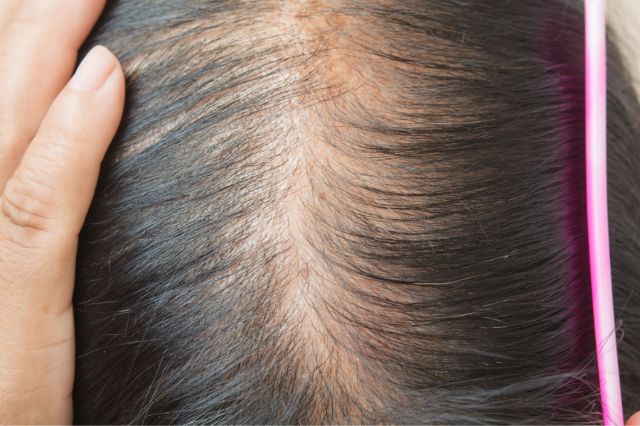
Hair thinning and excessive shedding affects a significant number of women in their lifetime. While it’s commonly associated with male pattern baldness, the reality is women’s hair thinning occurs frequently due to multiple reasons. But tackling it starts with understanding the underlying triggers.
Let’s explore some of the most common culprits behind women with thinning hair along with effective treatment options for reversing and managing this distressing condition.
Understanding Hair Thinning in Women
Hair thinning, also known as female pattern hair loss or androgenetic alopecia, is a gradual process in which the hair strands become progressively finer and shorter.
Unlike male pattern baldness, which often results in a receding hairline or a bald spot on the crown, women with thinning hair typically experience diffuse thinning across the entire scalp.
Causes of Hair Thinning in Women
Female hair loss takes on various patterns ranging from all-over thinning to concentrated shedding at the crown or temples. Some key factors that promote hair thinning women experience include:
Hormonal Imbalances
Perhaps the predominant trigger, hormone shifts, and imbalances involving estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and thyroid levels significantly impact the hair growth cycle.
Drastic fluctuations like those occurring during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause or conditions like PCOS frequently spark diffuse shedding or thinning hair in women. Even certain birth control pills influence hormones regulating follicle growth cycles.
Physiological Stressors
Experiencing high fevers, recovering from significant injuries or surgeries, or managing chronic medical conditions can impose physiological stress on the body. This stress can temporarily disrupt the hair growth cycle, causing more hair follicles to prematurely enter their resting (telogen) phase.
As a result, individuals may notice excessive hair shedding, a concerning symptom for many.
Strict Dieting and Nutritional Deficiencies
Adhering to extreme diets that result in calorie deprivation or significant protein/nutrient deficits can lead to female hair thinning over time. The body requires a well-rounded intake of nutrients to sustain healthy hair growth.
Specifically, insufficient levels of iron, vitamin D, zinc, and amino acids are known to limit the body’s ability to produce new hair strands, contributing to thinning hair.
Emotional Stress
Periods of severe emotional distress, including experiences of anxiety, grief, or depression, can have a profound impact on various physiological pathways within the body. The production of high levels of stress hormones can disrupt the normal functioning of hair follicles, leading to noticeable hair loss.
Traction Alopecia
Certain hairstyling practices can also contribute to hair loss. Over-styling, the use of excessive heat, chemical treatments, and the adoption of tight hairstyles can cause localized breakage and lead to traction alopecia. This condition results from the constant pulling on hair roots, causing damage over time.
Autoimmune Conditions
Certain hairstyling practices can also contribute to hair loss. Over-styling, the use of excessive heat, chemical treatments, and the adoption of tight hairstyles can cause localized breakage and lead to traction alopecia. This condition results from the constant pulling on hair roots, causing damage over time.
Genetics
The genetic predisposition to female pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is another significant factor influencing hair health. This condition, driven by hormonal changes, typically results in thinning hair concentrated on the crown, with the pattern of hair loss often running in families, indicating a strong genetic link.
Effectively Treating Hair-Thinning Women Experience
There are a variety of solutions that help stabilize and regrow thinning hair in women, depending on the underlying trigger:
Medications
The FDA-approved topical treatment minoxidil (Rogaine) is widely used to counteract hormonal issues and genetic thinning. Minoxidil is particularly effective in addressing hormonal issues and genetic predispositions to thinning hair, working by stimulating dormant hair follicles to re-enter an active growth phase.
Prescription anti-androgen therapies offer another avenue for combatting female pattern baldness by blocking male hormones implicated in hair loss. Treatments may include hormonal creams and pills, though some healthcare providers may also recommend medications like spironolactone or finasteride for long-term management.
In cases where autoimmune conditions trigger hair loss, medications designed to moderate the immune system can be beneficial in halting hair loss and encouraging regrowth.
Laser Therapy
Low-level laser therapy utilizes specific wavelengths of light to energize hair follicles, encouraging them to return to the growth phase. Devices for home use, such as laser combs or wearable laser caps, have shown promise in stimulating regrowth for women experiencing general thinning or localized bald spots.
Infrared light therapy, in particular, has been noted for its ability to rejuvenate follicular cellular metabolism, potentially prolonging the hair growth phase.
Hair Loss Concealers and Extensions
While waiting for medical or therapeutic treatments to take effect, cosmetic solutions offer an immediate, though temporary, fix. Products such as camouflaging sprays, powders, and volumizers can effectively conceal thinning areas. For those seeking a more lasting solution, hair extensions can provide coverage and added volume.
Surgical Options
Hair transplant surgery stands as a permanent solution for severe cases of hair thinning, where the goal is to restore scalp density. This procedure involves transplanting healthy follicles from denser areas of the scalp to the thinning sections.
Techniques like Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) are favored for their ability to deliver natural-looking results, though they come at a higher cost.
Natural Solutions
There are also natural remedies like scalp massages known to stimulate circulation and balance hormone levels impacting growth. Essential oils, herbal extracts and multi-vitamins likewise help fortify follicle function.
Conventional treatments combined with lifestyle tweaks stabilize many women’s thinning hair by addressing root triggers like stress, nutritional deficits, and excessive styling damage.
Protecting Against Further Hair Thinning
While managing a troubling trigger, several proactive tactics help ward off preventable thinning or worsening hair loss in women:
- Being gentle washing, brushing, and avoiding tight hairstyles minimizes traction
- Allowing hair breaks between chemical treatments, excessive heat styling
- Eating a nutrient-balanced diet with sufficient protein, iron, and biotin
- Taking daily hair vitamins bolstering follicle health
- Exploring natural botanicals like rosemary oil or saw palmetto for gentle regrowth
Controlling Stress
Given significant connections with stress, it’s important for women to maintain strong coping strategies for stress management through routines like:
- Meditation and deep breathing
- Getting sufficient quality sleep
- Engaging in regular exercise like yoga
- Pursuing enjoyable hobbies
- Speaking to a therapist when needed
Developing self-care regimens and coping with anxiety ultimately create physiological balance which in turn benefits hair quality.
The Road to Restored Volume and Confidence
While thinning hair in women often reflects transient hormonal or physiologic states like post-pregnancy or high stress periods, persistently excessive shedding mandates interventions. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment gets thinning under control before permanent or harder to reverse baldness develops.
Women experiencing hair thinning don’t have to resign themselves to insecurity or conceal themselves with unrealistic hairpieces. By identifying underlying triggers, the range of medications, therapies, and natural solutions can re-establish fuller, thicker locks.
For many women, restoring hair volume and luster rekindles confidence that radiates through daily life. When complemented with diligent scalp care, stress management, and sustaining follicle health, hair thinning becomes a surmountable challenge.
At the end of the day, attentive self-care ensures not just strong, shiny manes, but amplified self-assuredness in putting that glorious hair forward for the world to admire.